Simulation
Simulation is a technique in programming where all events are processed in the order of occurrence. By translating real world logic into programming code, simulation speeds up tasks that may otherwise take a long time for human. Simulation does not provide alternative shortcuts to a solution; it simply speeds up the process.
Example
Problem
Given 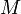 trees and the number of days each tree takes to grow a fruit, compute the total number of fruits after
trees and the number of days each tree takes to grow a fruit, compute the total number of fruits after 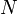 days.
days.
Solution
For each tree 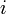 , keep a variable
, keep a variable 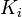 indicating the number of days it takes for the next fruit to grow. Simulate the situation day by day. On each day, decrease
indicating the number of days it takes for the next fruit to grow. Simulate the situation day by day. On each day, decrease 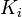 by 1 and increase the fruit count by the number of
by 1 and increase the fruit count by the number of 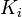 's that equal zero, and reset these
's that equal zero, and reset these 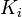 's. Output the total sum at the end.
's. Output the total sum at the end.
Analysis
This solution gives the correct answer, in 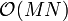 time. This is fine if
time. This is fine if 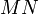 is small, but a better technique is required if
is small, but a better technique is required if 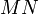 is large.
is large.
Characteristics
When a problem is logically simple and can be directly done by human, simulation is very likely the solution. When the bounds on variables are small, simulation is a quick, safe, and convincing technique. When run time is a concern, other techniques such as dynamic programming may be required.