Difference between revisions of "Knuth–Morris–Pratt algorithm"
(Created page with "The '''Knuth–Morris–Pratt (KMP) algorithm''' is a linear time solution to the single-pattern string search problem. It is based on the observation that a partial match gi...") |
(No difference)
|
Revision as of 08:29, 3 April 2011
The Knuth–Morris–Pratt (KMP) algorithm is a linear time solution to the single-pattern string search problem. It is based on the observation that a partial match gives useful information about whether or not the needle may partially match subsequent positions in the haystack. This is because a partial match indicates that some part of the haystack is the same as some part of the needle, so that if we have preprocessed the needle in the right way, we will be able to draw some conclusions about the contents of the haystack (because of the partial match) without having to go back and re-examine characters already matched. In particular, this means that, in a certain sense, we will want to precompute how the needle matches itself. The algorithm thus "never looks back" and makes a single pass over the haystack. Together with linear time preprocessing of the needle, this gives a linear time algorithm overall.
Motivation
The motivation behind KMP is best illustrated using a few simple examples.
Example 1
In this example, we are searching for the string  = aaa in the string
= aaa in the string  = aaaaaaaaa (in which it occurs seven times). The naive algorithm would begin by comparing
= aaaaaaaaa (in which it occurs seven times). The naive algorithm would begin by comparing 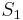 with
with 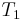 ,
, 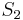 with
with 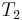 , and
, and 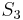 with
with 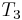 , and thus find a match for
, and thus find a match for  at position 1 of
at position 1 of  . Then it would proceed to compare
. Then it would proceed to compare 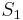 with
with 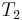 ,
, 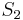 with
with 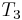 , and
, and 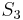 with
with 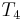 , and thus find a match at position 2 of
, and thus find a match at position 2 of  , and so on, until it finds all the matcsubstringhes. But we can do better than this, if we preprocess
, and so on, until it finds all the matcsubstringhes. But we can do better than this, if we preprocess  and note that
and note that 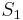 and
and 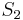 are the same, and
are the same, and 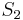 and
and  are the same. That is, the prefix of length 2 in
are the same. That is, the prefix of length 2 in  matches the substring of length 2 starting at position 2 in
matches the substring of length 2 starting at position 2 in  ;
;  partially matches itself. Now, after finding that
partially matches itself. Now, after finding that 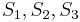 match
match 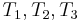 , respectively, we no longer care about
, respectively, we no longer care about 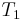 , since we are trying to find a match at position 2 now, but we still know that
, since we are trying to find a match at position 2 now, but we still know that 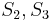 match
match 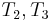 respectively. Since we already know
respectively. Since we already know 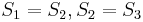 , we now know that
, we now know that 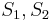 match
match 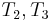 respectively; there is no need to examine
respectively; there is no need to examine 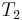 and
and 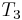 again, as the naive algorithm would do. If we now check that
again, as the naive algorithm would do. If we now check that 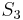 matches
matches 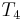 , then, after finding
, then, after finding  at position 1 in
at position 1 in  , we only need to do one more comparison (not three) to conclude that
, we only need to do one more comparison (not three) to conclude that  also occurs at position 2 in
also occurs at position 2 in  . So now we know that
. So now we know that 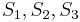 match
match 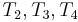 , respectively, which allows us to conclude that
, respectively, which allows us to conclude that 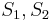 match
match 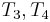 . Then we compare
. Then we compare 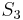 with
with 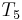 , and find another match, and so on. Whereas the naive algorithm needs three comparisons to find each occurrence of
, and find another match, and so on. Whereas the naive algorithm needs three comparisons to find each occurrence of  in
in  , our technique only needs three comparisons to find the first occurrence, and only one for each after that, and doesn't go back to examine previous characters of
, our technique only needs three comparisons to find the first occurrence, and only one for each after that, and doesn't go back to examine previous characters of  again. (This is how a human would probably do this search, too.
again. (This is how a human would probably do this search, too.
Example 2
Now let's search for the string  = aaa in the string
= aaa in the string  = aabaabaaa. Again, we start out the same way as in the naive algorithm, hence, we compare
= aabaabaaa. Again, we start out the same way as in the naive algorithm, hence, we compare 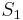 with
with 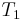 ,
, 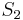 with
with 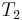 , and
, and 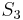 with
with 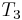 . Here we find a mismatch between
. Here we find a mismatch between  and
and  , so
, so  does not occur at position 1 in
does not occur at position 1 in  . Now, the naive algorithm would continue by comparing
. Now, the naive algorithm would continue by comparing 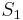 with
with 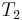 and
and 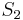 with
with 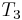 , and would find a mismatch; then it would compare
, and would find a mismatch; then it would compare 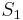 with
with 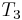 , and find a mismatsubstringch, and so on. But a human would notice that after the first mismatch, the possibilities of finding
, and find a mismatsubstringch, and so on. But a human would notice that after the first mismatch, the possibilities of finding  at positions 2 and 3 in
at positions 2 and 3 in  are extinguished. This is because, as noted in Example 1,
are extinguished. This is because, as noted in Example 1, 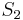 is the same as
is the same as 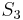 , and since
, and since 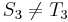 ,
, 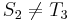 also (so we will not find
also (so we will not find  at position 2 of
at position 2 of  ). And, likewise, since
). And, likewise, since 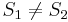 , and
, and 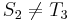 , it is also true that
, it is also true that 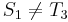 , so it is pointless looking for a match at the third position of
, so it is pointless looking for a match at the third position of  . Thus, it would make sense to start comparing again at the fourth position of
. Thus, it would make sense to start comparing again at the fourth position of  (i.e.,
(i.e., 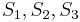 with
with 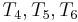 , respectively). Again finding a mismatch, we use similar reasoning to rule out the fifth and sixth positions in
, respectively). Again finding a mismatch, we use similar reasoning to rule out the fifth and sixth positions in  , and begin matching again at
, and begin matching again at 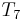 (where we finally find a match.) Again, notice that the characters of
(where we finally find a match.) Again, notice that the characters of  were examined strictly in order.
were examined strictly in order.
Example 3
As a more complex example, imagine searching for the string  = tartan in the string
= tartan in the string  = tartaric_acid. We make the observation that the prefix of length 2 in
= tartaric_acid. We make the observation that the prefix of length 2 in  matches the substring of length 2 in
matches the substring of length 2 in  starting from position 4. Now, we start by comparing
starting from position 4. Now, we start by comparing 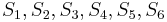 with
with 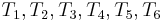 , respectively. We find that
, respectively. We find that 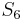 does not match
does not match 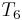 , so there is no match at position 1. At this point, we note that since
, so there is no match at position 1. At this point, we note that since 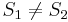 and
and 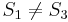 , and
, and 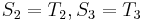 , obviously,
, obviously, 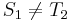 and
and 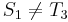 , so there cannot be a match at position 2 or position 3. Now, recall that
, so there cannot be a match at position 2 or position 3. Now, recall that 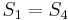 and
and 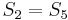 , and that
, and that 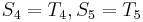 . We can translate this to
. We can translate this to 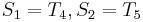 . So we proceed to compare
. So we proceed to compare 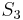 with
with 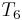 . In this way, we have ruled out two possible positions, and we have restarted comparing not at the beginning of
. In this way, we have ruled out two possible positions, and we have restarted comparing not at the beginning of  but in the middle, avoiding re-examining
but in the middle, avoiding re-examining 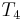 and
and 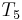 .
.
Concept
The examples above show that the KMP algorithm relies on noticing that certain substrings of the needle match or do not match other substrings of the needle, but it is probably not clear what the unifying organizational principle for all this match information is. Here it is:
- At each position
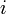 of
of  , find the longest substring of
, find the longest substring of  ending at
ending at 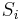 which is also a prefix of
which is also a prefix of  .
.
We shall denote the length of this substring by 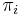 , following [1].
, following [1].
The table 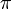 uses linear space, and, as we shall see, can be computed in linear time. It contains all the information we need in order to execute the "smart" searching techniques described in the examples. In particular, in examples 1 and 2, we used the fact that
uses linear space, and, as we shall see, can be computed in linear time. It contains all the information we need in order to execute the "smart" searching techniques described in the examples. In particular, in examples 1 and 2, we used the fact that 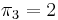 , that is, the prefix aa matches the suffix aa. In example 3, we used the facts that
, that is, the prefix aa matches the suffix aa. In example 3, we used the facts that 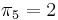 . This tells us that the prefix ta matches the substring ta ending at the fifth position. In general, the table
. This tells us that the prefix ta matches the substring ta ending at the fifth position. In general, the table 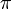 tells us, after either a successful match or a mismatch, what the next position is that we should check in the haystack. Comparison proceeds from where it was left off, never revisiting a character of the haystack after we have examined the next one.
tells us, after either a successful match or a mismatch, what the next position is that we should check in the haystack. Comparison proceeds from where it was left off, never revisiting a character of the haystack after we have examined the next one.
References
- ↑ Thomas H. Cormen; Charles E. Leiserson, Ronald L. Rivest, Clifford Stein (2001). "Section 32.4: The Knuth-Morris-Pratt algorithm". Introduction to Algorithms (Second ed.). MIT Press and McGraw-Hill. pp. 923–931. ISBN 978-0-262-03293-3.