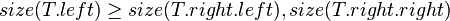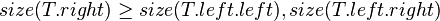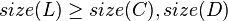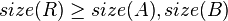Difference between revisions of "Size Balanced Tree"
(Correct quote) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | A '''size balanced tree''' ('''SBT''') is a [[self-balancing binary search tree]] ( | + | A '''size balanced tree''' ('''SBT''') is a [[self-balancing binary search tree]] (SBBST) first published by Chinese student Qifeng Chen in 2007. The tree is rebalanced by examining the sizes of each node's subtrees. It is not to be confused with [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Weight-balanced_tree weight-balanced trees], which have a slightly different set of balancing properties to be maintained. |
| + | |||
| + | The only extra piece of information that needs to be stored at each node is the size of the subtree (compared to "useless" fields such as randomized weights in treaps or colours in red–black tress), this makes it very convenient to implement the ''select-by-rank'' and ''get-rank'' operations that implement an [[order statistic tree]]. It also supports the standard binary search tree operations such as insertion, deletion, and searching in O(log ''n'') time. According to Chen's paper, "it works much faster than many other famous BSTs due to the tendency of a perfect BST in practice."<ref>Chen, Qifeng. [http://www.scribd.com/doc/3072015/ "Size Balanced Tree"], Guandong, China, 29 December 2006.</ref> | ||
==Properties== | ==Properties== | ||
Latest revision as of 18:37, 10 August 2019
A size balanced tree (SBT) is a self-balancing binary search tree (SBBST) first published by Chinese student Qifeng Chen in 2007. The tree is rebalanced by examining the sizes of each node's subtrees. It is not to be confused with weight-balanced trees, which have a slightly different set of balancing properties to be maintained.
The only extra piece of information that needs to be stored at each node is the size of the subtree (compared to "useless" fields such as randomized weights in treaps or colours in red–black tress), this makes it very convenient to implement the select-by-rank and get-rank operations that implement an order statistic tree. It also supports the standard binary search tree operations such as insertion, deletion, and searching in O(log n) time. According to Chen's paper, "it works much faster than many other famous BSTs due to the tendency of a perfect BST in practice."[1]
Contents
Properties
The size balanced tree examines each node's size (i.e. the number of nodes below it in the subtree) to determine when rotations should be performed. Each node  in the tree satisfies the following two properties:
in the tree satisfies the following two properties:
In other words, each child node of  is not smaller in size than the child nodes of its sibling. Clearly, we should consider the sizes of nonexistent children and siblings to be 0.
is not smaller in size than the child nodes of its sibling. Clearly, we should consider the sizes of nonexistent children and siblings to be 0.
Consider the following example where  is the node in question,
is the node in question, 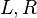 are its child nodes, and
are its child nodes, and 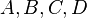 are subtrees which also satisfy the above SBT properties on their own.
are subtrees which also satisfy the above SBT properties on their own.
T
/ \
/ \
L R
/ \ / \
A B C D
Then, the node  must satisfy:
must satisfy:
Rotations
The rotations of SBTs are analogous to those in other self-balancing binary search trees.
------------- Right Rotation ------------
| Q | ---------------> | P |
| / \ | | / \ |
-- P C | | A Q --
/ \ <--- Left Rotation ---> / \
A B <--------------- B C
Left Rotation
def left-rotate(t):
k ← t.right
t.right ← k.left
k.left ← t
k.size ← t.size
t.size ← t.left.size + t.right.size + 1
t ← k
Right Rotation
def right-rotate(t):
k ← t.left
t.left ← k.right
k.right ← t
k.size ← t.size
t.size ← t.left.size + t.right.size + 1
t ← k
Maintenance
After insertions and deletions, the new sizes of subtrees may violate the two properties above. Thus, we define a procedure maintain(T) to rebalance the SBT rooted at the node  . This should be called with the precondition that
. This should be called with the precondition that  's children are already SBTs themselves. Since property 1 and 2 are symmetrical, we will only discuss property 1.
's children are already SBTs themselves. Since property 1 and 2 are symmetrical, we will only discuss property 1.
There are 4 cases to consider when rebalancing.
- Case 1:
- Perhaps after inserting a value to
 , the scenario below (figure 1) may occur, leading to
, the scenario below (figure 1) may occur, leading to 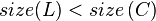 .
. - To fix this, we first perform a
right-rotateon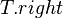 (figure 2) and then a
(figure 2) and then a left-rotateon (figure 3).
(figure 3).
Fig. 1: Fig. 2: Fig. 3:
insert(R,v) right-rotate(R) left-rotate(T)
T T C
/ \ / \ / \
/ \ / \ / \
L R L C T R
/ \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \
A B C D A B E R L E F D
/ \ / \ / \
E F F D A B
- After these operations, the properties of the entire tree in figure 3 becomes unpredictable. Luckily, the subtrees
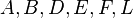 are still SBTs. Thus, we can recursively call
are still SBTs. Thus, we can recursively call maintainon subtrees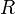 and
and  to take care of them.
to take care of them. - Now that all of the subtrees are SBTs, we still have to make sure that the root node
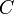 satisfies the SBT properties. So, we call
satisfies the SBT properties. So, we call maintainone last time on root node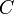 .
.
- Case 2:
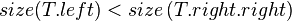
- Perhaps after inserting a value to
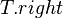 , the scenario below (figure 4) may occur, leading to
, the scenario below (figure 4) may occur, leading to 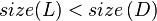 . This is similar to case 1, except that instead of going below
. This is similar to case 1, except that instead of going below 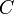 ,
, 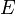 and
and 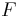 instead goes below
instead goes below 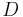 . We can omit them from the diagram.
. We can omit them from the diagram. - Fixing this, we will perform a
left-rotateon the root node , obtaining the structure in figure 5.
, obtaining the structure in figure 5.
Fig. 4: Fig. 5:
insert(R,v) left-rotate(T)
T R
/ \ / \
/ \ / \
L R T D
/ \ / \ / \
A B C D L C
/ \
A B
- After this, the tree rooted at R is still not yet a SBT because
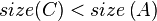 or
or 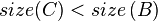 may be true. So, we continue to call
may be true. So, we continue to call maintainon .
. - Now that we have satisfied the precondition of making
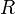 's subtrees SBTs, we may call
's subtrees SBTs, we may call maintainon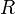 itself.
itself.
- Case 3:
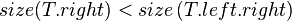
- Symmetrical to case 1.
- Case 4:
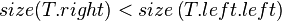
- Symmetrical to case 2.
With this casework being taken care of, it becomes straightforward to actually implement maintain.
def maintain(t):
if t.left.size < t.right.left.size: //case 1
right-rotate(t.right)
left-rotate(t)
maintain(t.left)
maintain(t.right)
maintain(t)
else if t.left.size < t.right.right.size: //case 2
left-rotate(t)
maintain(t.left)
maintain(t)
else if t.right.size < t.left.right.size: //case 1'
left-rotate(t.left)
right-rotate(t)
maintain(t.left)
maintain(t.right)
maintain(t)
else if t.right.size < t.left.left.size: //case 2'
right-rotate(t)
maintain(t.right)
maintain(t)
This pseudocode is slightly slow and redundant. Since we know that the two SBT properties will usually be satisfied, the following is an optimization.
Simply add an extra boolean flag to the maintain parameters, indicating whether cases 1/2 or their symmetrical cases are being examined.
If the flag is TRUE, then we examine cases 1 and 2, otherwise we examine cases 3 and 4. Doing so will eliminate many unnecessary comparisons.
def maintain(t, flag):
if flag:
if t.left.size < t.right.left.size: //case 1
right-rotate(t.right)
left-rotate(t)
else if t.left.size < t.right.right.size: //case 2
left-rotate(t)
else:
done
else:
if t.right.size < t.left.right.size: //case 1'
left-rotate(t.left)
right-rotate(t)
else if t.right.size < t.left.left.size: //case 2'
right-rotate(t)
else:
done
maintain(t.left, FALSE) //maintain the left subtree
maintain(t.right, TRUE) //maintain the right subtree
maintain(t, TRUE) //maintain the whole tree
maintain(t, FALSE) //maintain the whole tree
The proof for why maintain(t.left, TRUE) and maintain(t.right, FALSE) are unnecessary can be found in section 6 of Chen's paper. Furthermore, the running time of maintain is O(1) amortized (which means that you do not have to worry about it not terminating).
Fundamental Operations
Searching
Searching in SBTs is exactly the same as searching in other binary search trees. The following iterative implementation will return a pointer to the node in the SBT rooted at 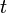 which has key
which has key 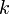 .
.
def search(t, k):
x ← t
while x is not NIL:
if k < x.key then x ← x.left
else if x.key < k then x ← x.right
else return x
return NIL //key not found!
Get Max/Min
The size of the SBT is already stored. These operations can thus be handled trivially by the select operation implemented in the section below.
Iteration
Iterating a SBT is exactly the same as iterating a normal binary search tree (by repeatedly finding nodes' predecessors/successors).
Insertion
Inserting into a SBT is very simple. The only difference from normal binary search trees is that it has an extra call to maintain at the end. The following recursive version will insert the node 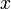 into the SBT rooted at
into the SBT rooted at 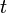 .
.
def insert(t, x):
if x is NIL:
t ← x
else
t.size ← t.size + 1
if x.key < t.key:
insert(t.left, x)
else
insert(t.right, x)
maintain(t, x.key ≥ t.key)
Deletion
Deletion is exactly the same as in normal binary search trees. It is not even necessary to call maintain afterwards. The proof for this is as follows: A SBT will have all of its properties before deletion. Even though we cannot guarantee that the SBT will retain its balanced properties after the insertion, we know for sure that its height (and thus, its running time) will not increase. Given this, it is clear that calling maintain after deleting is extraneous.
Order Statistics
Since SBTs already conveniently store the 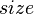 field to maintain balance, nothing else is needed to transform it into a fully-fledged order statistics tree.
field to maintain balance, nothing else is needed to transform it into a fully-fledged order statistics tree.
Select
The following function returns a pointer to the 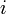 th smallest element in the SBT rooted at
th smallest element in the SBT rooted at 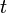 , where
, where 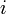 is zero-indexed. To make this one-indexed, simply change "
is zero-indexed. To make this one-indexed, simply change "r ← t.left.size" to "r ← t.left.size + 1" and "i - (r + 1)" to "i - r".
def select(t, i):
r ← t.left.size
if i = r:
return t
else if i < r:
return select(t.left, i)
else
return select(t.right, i - (r + 1))
Rank
Determining the rank of an element in a SBT is exactly the same as doing so for a regular binary search tree.
References
- ↑ Chen, Qifeng. "Size Balanced Tree", Guandong, China, 29 December 2006.